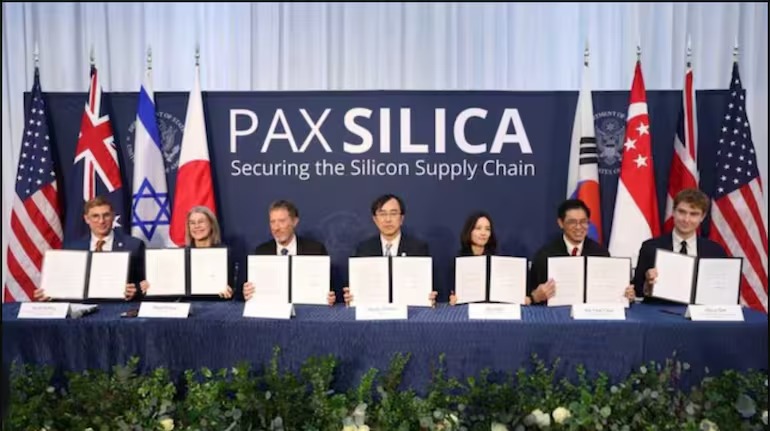
In a move set to redefine the global technological landscape, India formally joined Pax Silica—the United States’ premier strategic initiative on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and supply chain security—on Friday. The signing of the “Pax Silica Declaration” took place on the sidelines of the Global AI Impact Summit 2026, signaling a powerful new economic security consensus between the world’s two largest democracies. Launched by the U.S. Department of State in late 2025, Pax Silica (meaning “Silicon Peace”) is a strategic framework designed to build a secure, resilient, and innovation-driven supply chain. It focuses on the entire “silicon stack,” ranging from critical minerals and semiconductor manufacturing to the deployment of advanced AI infrastructure. By joining this alliance, India aligns with a “trusted network” of partners—including Australia, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and the UK—to reduce coercive dependencies and ensure that the commanding heights of the global economy are governed by free and open societies.
“Today, with India’s entry into Pax Silica, we choose to win. It is about whether innovation happens in Bengaluru and Silicon Valley or in surveillance states.”
Union Minister for Electronics and IT Ashwini Vaishnaw described the pact as a “historic milestone” that will supercharge India’s domestic semiconductor mission. He highlighted India’s rapid ascent in the field; Indian engineers are already designing cutting-edge. Ten semiconductor plants are currently being established in India, with the first poised for commercial production soon.
India aims to provide the 1 million skilled workers required globally by the semiconductor industry over the next decade. In tandem with the Pax Silica signing, India unveiled the New Delhi Frontier AI Commitments. This voluntary framework, adopted by leading global tech giants (including Google’s Sundar Pichai and OpenAI’s Sam Altman) and Indian firms, focuses on two key pillars: Participating companies will publish anonymized statistical insights on how AI is diffusing through the economy to help governments craft better policies for jobs and education.
A dedicated push to evaluate and develop AI systems in under-represented languages and cultural contexts, ensuring that the “AI revolution” does not leave the Global South behind. The partnership marks a shift toward treating technological supply chains as vital national security interests. By securing access to critical minerals and high-end hardware, India and its partners aim to insulate their economies from “weaponized dependencies” and technological blackmail.